

When administering hypertonic saline, frequent serum sodium controls must be conducted so that treatment can be adjusted accordingly. Treatment of cerebral edema (see “ ICP management”).Hypertonic IV crystalloids ( hypertonic saline) Hypertonic saline solutions must be administered with extreme caution because of the risk of rapid osmotic changes. Maintenance fluid therapy with hypotonic solutions can cause iatrogenic hyponatremia and cerebral edema. Solvent for IV drugs (e.g., noradrenaline infusions).Maintenance fluid therapy in specific cases.

MAINTENANCE FLUID CALCULATOR FREE
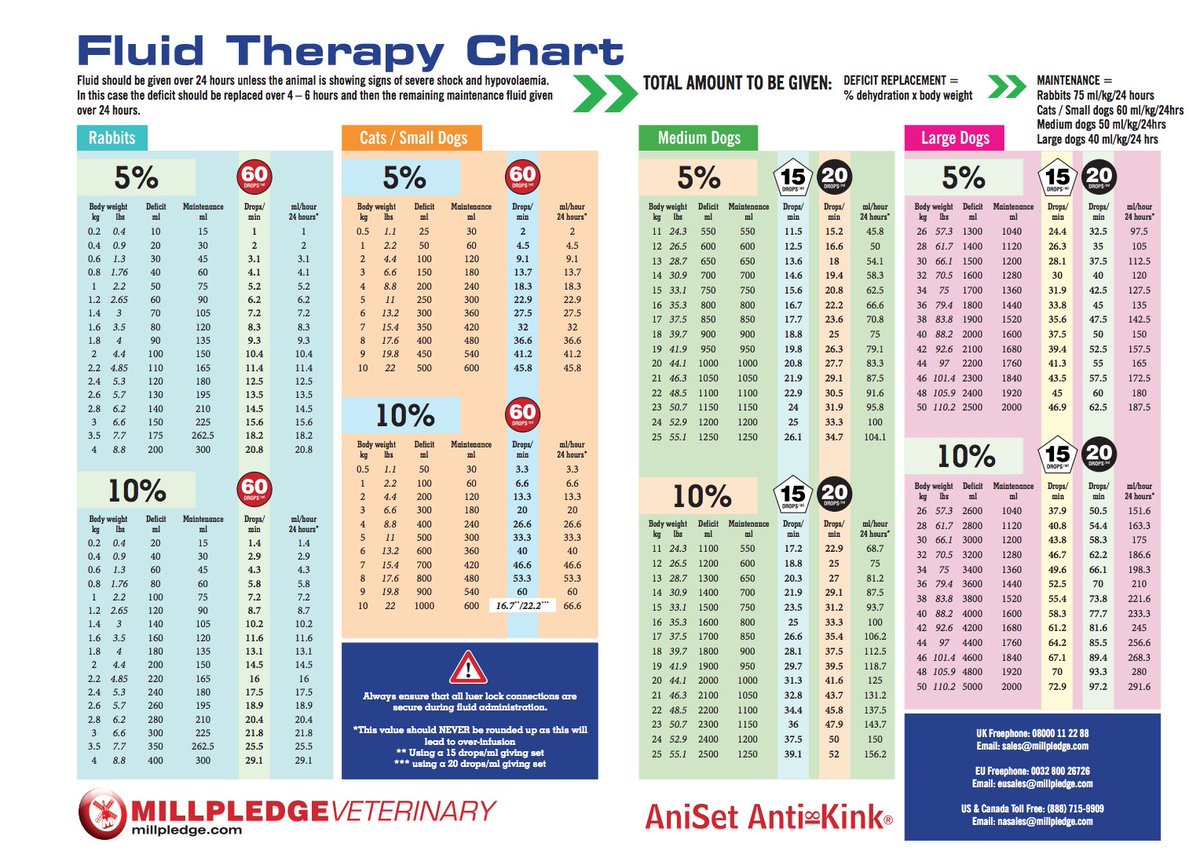
The most commonly used fluids in a hospital setting.Aqueous solutions with varying concentrations of electrolytes.The tonicity of a solution is determined by the solutes that do not enter the cell and are, therefore, osmotically active (e.g., sodium, potassium). The osmolarity of a parenteral solution takes into account the concentration of all the solutes, including those that enter cells (e.g., dextrose). The osmolarity and tonicity of a solution are not the same thing! Administering solutions with inappropriate tonicity can lead to life-threatening fluid and electrolyte imbalances. Higher than the intracellular compartmentĬan be hypertonic, isotonic, or hypotonic Describes what will happen to the equilibrium of a cell when it is placed in a certain solutionĮquivalent to the intracellular compartment.Reflects the osmotic effect of particles that cannot easily pass cell membranes, i.e., the effective osmotic pressure gradient.Tonicity: the capacity of an extracellular fluid to create an osmotic gradient that will cause water to move into or out of the intracellular compartment cannot be measured and has no units.Takes into account all osmotically active particles, including those that enter cells (e.g., glucose, urea).Preferred term to describe the osmotic pressure of parenteral fluids.Osmolarity: the concentration of solutes per unit volume of solvent (mOsm/ L) often used interchangeably with osmolality in clinical practice.Osmolality: the concentration of dissolved particles per unit mass of solution (mOsm/ kg) preferred term to describe the osmotic pressure of biological systems.Balanced IV fluid solutions: crystalloids or colloids that do not significantly alter the homeostasis of the extracellular compartment.Colloids: solutions that contain larger molecular weight solutes (e.g., albumin and starch).Crystalloids: solutions that contain small molecular weight solutes (e.g., minerals, dextrose).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
